In this application note, the Advion expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) coupled with the Advion AVANT™ UHPLC (LC/CMS) was used to measure the concentration of cannabinoids from commercially available CBD oils for a comparative test against the product labels.
The research in this application note was published in Cannabis Science & Technology Magazine May/June 2019 and presented at the 2019 Cannabis Science Conference East in Baltimore, MD.
Introducing a new way to analyze and present mass spectral data, the Advion Interchim Scientific® Peak Express® patented software uses the delta spectrum (ΔS) to quickly and automatically detect significant peaks within mass spectra based on their relative change in intensity over time instead of their absolute intensity.
- Find impurities and minor components that would otherwise be missed
- Find unknowns in complex samples such as natural products
- Automatically find adducts, dimers, fragments, side reactions, and other unexpected compounds in real time and post processing
- Control mass-directed purification without providing an exact mass
- Get extracted ion chromatogram (XIC) quality data while scanning the entire mass range
USDA-ARS, Cornell University, Michigan State University
Abstract

The common dry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) is a globally produced pulse crop and an important source of micronutrients for millions of people across Latin America and Africa. Many of the preferred black and red seed types in these regions have seed coat polyphenols that inhibit the absorption of iron. Yellow beans are distinct from other market classes because they accumulate the antioxidant kaempferol 3-glucoside in their seed coats. Due to their fast cooking tendencies, yellow beans are often marketed at premium prices in the same geographical regions where dietary iron deficiency is a major health concern. Hence, this study compared the iron bioavailability of three faster cooking yellow beans with contrasting seed coat colors from Africa (Manteca, Amarillo, and Njano) to slower cooking white and red kidney commercial varieties. Iron status and iron bioavailability was assessed by the capacity of a bean based diet to generate and maintain total body hemoglobin iron (Hb-Fe) during a 6 week in vivo (Gallus gallus) feeding trial. Over the course of the experiment, animals fed yellow bean diets had significantly (p ≤ 0.05) higher Hb-Fe than animals fed the white or red kidney bean diet. This study shows that the Manteca yellow bean possess a rare combination of biochemical traits that result in faster cooking times and improved iron bioavailability. The Manteca yellow bean is worthy of germplasm enhancement to address iron deficiency in regions where beans are consumed as a dietary staple.
Analysis was performed by LC/MS using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Thanks to the diminishing size and cost of mass spectrometers, coupled with their increasing robustness and ease of use, universities are now starting to furnish their undergraduate chemistry laboratories with this advanced analytic tool.
“My favorite learning environment is the laboratory,” explains Paul A. Flowers, professor of analytical chemistry at University of North Carolina at Pembroke. “I like teaching students fundamentals through bona fide research experiences.” Flowers began using mass spectrometry in the teaching laboratory about six years ago and hasn’t looked back.
Learn more about the integration of mass spectrometry for teaching with this free whitepaper.
We demonstrate a cost-effective UHPLC/CMS method for the analysis of chloramphenicol in milk with a detailed discussion of sensitivity, linear response range, carryover and robustness using the Advion expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) and Advion AVANT™ UHPLC System.
This application note was adapted from a poster that was presented at the 2019 ASMS Conference on Mass Spectrometry and Allied Topics in Atlanta, GA.
National Institutes of Health
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Cancer Institute
Abstract
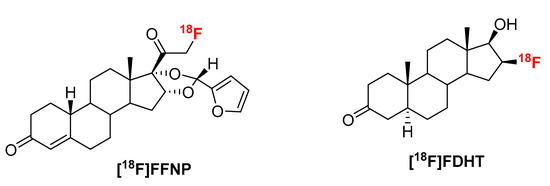
To further explore the scope of our recently developed “fluorination on Sep-Pak” method, we prepared two well-known positron emission tomography (PET) tracers 21-[18F]fluoro-16α,17α-[(R)-(1′-α-furylmethylidene)dioxy]-19-norpregn-4-ene-3,20-dione furanyl norprogesterone ([18F]FFNP) and 16β-[18F]fluoro-5α-dihydrotestosterone ([18F]FDHT). Following the “fluorination on Sep-Pak” method, over 70% elution efficiency was observed with 3 mg of triflate precursor of [18F]FFNP. The overall yield of [18F]FFNP was 64–72% (decay corrected) in 40 min synthesis time with a molar activity of 37–81 GBq/µmol (1000–2200 Ci/mmol). Slightly lower elution efficiency (~55%) was observed with the triflate precursor of [18F]FDHT. Fluorine-18 labeling, reduction, and deprotection to prepare [18F]FDHT were performed on Sep-Pak cartridges (PS-HCO3 and Sep-Pak plus C-18). The overall yield of [18F]FDHT was 25–32% (decay corrected) in 70 min. The molar activity determined by using mass spectrometry was 63–148 GBq/µmol (1700–4000 Ci/mmol). Applying this quantitative measure of molar activity to in vitro assays [18F]FDHT exhibited high-affinity binding to androgen receptors (Kd~2.5 nM) providing biological validation of this method.
Analysis was performed by Select Ion Monitoring (SIM) and LC/MS using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Using separation from the AVANT™ UHPLC system coupled to the expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS), cannabinoids from commercially available CBD oils are measured for concentration against product label claims for a comparative test.
This poster was presented at the 2019 Cannabis Science Conference East in Baltimore, MD.
We demonstrate a cost-effective UHPLC/CMS method for the analysis of chloramphenicol in milk with a detailed discussion of sensitivity, linear response range, carryover and robustness using the Advion expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) and Advion AVANT™ UHPLC System.
This poster was presented at the 2019 ASMS Conference on Mass Spectrometry and Allied Topics in Atlanta, GA.
Federico II University Medical School of Naples, University of Naples “Federico II”
Abstract
Vitamin D deficiency and obesity are two public health problems extensively exacerbated over the last years. Among the several mechanisms proposed to account for the complex interplay between vitamin D and obesity, one that has gained particular attention is related to the emerging role of obesity-related changes in gut microbiota and gut-derived metabolites, such as Trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO). Vitamin D deficiency and high circulating TMAO levels are associated with body weight and the severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Considering the link of obesity with vitamin D on the one hand and obesity with TMAO on the other hand, and the central role of the liver in both the vitamin D and TMAO metabolism, the aim of this cross-sectional observational study was first, to confirm the possible inverse association between vitamin D and TMAO across different body mass index (BMI) classes and second, to investigate if this association could be influenced by the presence of NAFLD. One hundred and four adult subjects (50 males and 54 females; 35.38 ± 7.49 years) were enrolled. The fatty liver index (FLI) was used as a proxy for the diagnosis of NAFLD. Vitamin D deficiency was found in 65 participants (62.5%), while 33 subjects (31.7%) had insufficient levels, and the remaining subjects had sufficient levels of vitamin D. Subjects with both vitamin D deficiency and FLI-NAFLD had the highest TMAO levels (p < 0.001). By stratifying the sample population according to the BMI classes, vitamin D levels decreased significantly along with the increase of plasma TMAO concentrations, with the lowest vitamin D levels and highest TMAO, respectively, in class III obesity. Vitamin D levels showed significant opposite associations with circulating levels of TMAO (r = −0.588, p < 0.001), but this association was no longer significant after the adjustment for FLI values. The highest values of TMAO were significantly associated with the severity of obesity (OR 7.92; p < 0.001), deficiency of vitamin D (OR 1.62; p< 0.001), and FLI-NAFLD (OR 3.79; p < 0.001). The most sensitive and specific cut-off for vitamin D to predict the circulating levels of TMAO was ≤19.83 ng/mL (p < 0.001). In conclusion, our study suggests that high TMAO levels are associated with vitamin D deficiency and NAFLD. Further studies are required to investigate if there is a causality link or whether all of them are simply the consequence of obesity.
Analysis was performed by LC/MS using the Advion expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
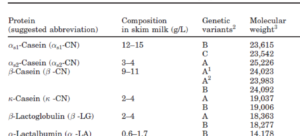
In this application note, the Advion Interchim Scientific® AVANT™ UHPLC/CMS system is used to analyze casein proteins in whole milk extract to separate and detect β-casein-B, -A1, and -A2, as well as K-casein and αs1-casein variants. This method is also suitable for a quick, relative quantitation of the β-casein-B, -A1, and -A2 variants in standards of β-casein.