Xention Limited, United Kingdom; University of Ljubljana, Slovenia
Abstract
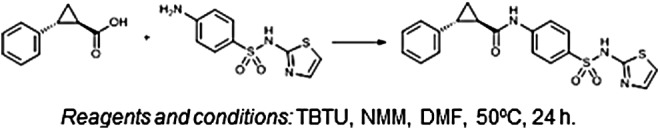
The rodent neuroblastoma cell line, ND7-23, is used to express voltage-dependent sodium (Nav) and other neuronal ion channels resistant to heterologous expression in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) or human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells. Their advantage is that they provide endogenous factors and signaling pathways to promote ion channel peptide folding, expression, and function at the cell surface and are also amenable to automated patch clamping. However, ND7-23 cells exhibit endogenous tetrodotoxin (TTX)-sensitive Nav currents, and molecular profiling has revealed the presence of Nav1.2, Nav1.3, Nav1.6, and Nav1.7 transcripts, but no study has determined which subtypes contribute to functional channels at the cell surface. In this publication, we profiled the repertoire of functional Nav channels endogenously expressed in ND7-23 cells using the QPatch automated patch clamp platform and selective toxins and small molecules.
Mass spec analysis was performed using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Mokpo National University, Gachon University, Hanyang University, Gachon Medical Research Institute, South Korea; University of Bremen, Germany
Abstract
G protein-coupled receptor (GPR) 119 is expressed in pancreatic β-cells and intestinal L cells, and is involved in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) release, respectively. Therefore, the development of GPR119 agonists is a potential treatment for type 2 diabetes. In this publication, screened 1500 natural plant extracts for GPR119 agonistic actions and investigated the most promising extract, that from Angelica dahurica (AD), for hypoglycemic actions in vitro and in vivo.
Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) data was measured using the Advion expression CMS
Gujarat University
Abstract
A library of thiosemicarbazide hybrid 2-(aldo-polyhydroxyalkyl)benzimidazole derivatives have been designed and synthesized with simple and eco-friendly methodologies. The structures of the compounds have been elucidated with the aid of elemental analysis, IR, mass and 1H NMR spectral data. These novel synthesized compounds have been evaluated for their antibacterial activity against two gram-positive bacteria (S. aureus and S. pyogenus) and two gram-negative bacteria (P. aeruginosa and E. coli). The title compounds have also been studied for their antifungal activity against C. albicans, A. niger and A. clavatus using the broth dilution technique.
Mass spec analysis was performed using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) with electrospray ionization (ESI).
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
Abstract
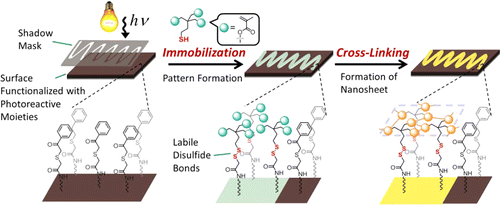
The preparation of cross-linked nanosheets with 1–2 nm thickness and predefined shape was achieved by lithographic immobilization of trimethacryloyl thioalkanoates onto the surface of Si wafers, which were functionalized with 2-(phenacylthio)acetamido groups via a photoinduced reaction. Subsequent cross-linking via free radical polymerization as well as a phototriggered Diels–Alder reaction under mild conditions on the surface led to the desired nanosheets. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS), as well as infrared reflection-absorption spectroscopy (IRRAS) confirmed the success of individual surface-modification and cross-linking reactions.
ESI-MS analysis was performed using the Advion Interchim Scientific® expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Gujarat University
Abstract
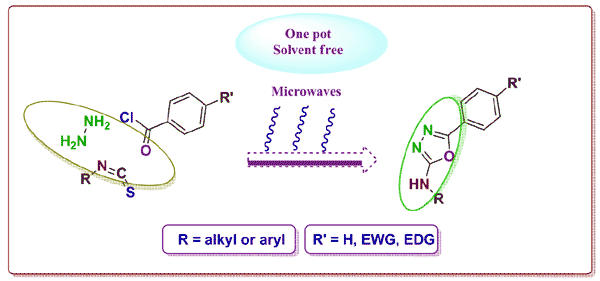
A convenient one-pot, multi-component and solvent free procedure for the preparation of substituted 2-amino-5-aryl-1,3,4-oxadiazoles has been achieved. The method is a significant improvement over previously reported synthesis. Reaction of acid chlorides with hydrazine hydrate and isothiocynates under microwave-irradiation (MWI) afforded the corresponding 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives in high yields with high purity. All synthesized compounds were characterized by FT-IR, proton and carbon NMR, mass spectroscopy and elemental analysis. A possible mechanism is proposed for the cyclodesulfurization based on the results of this study.
Mass spec analysis was performed on the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) using electrospray ionization (ESI).
Guru Ghasidas University, University of South Dakota
A one-pot practical, efficient, and environmentally benign multicomponent synthesis of 4H-pyrans and polysubstituted aniline derivatives of biological, pharmacological, and optical applications has been developed using a very mild, neutral, and reusable silica nanoparticles as catalyst. The 4H-pyran derivatives were synthesized by a three component reaction of an aldehyde, malononitrile, and 5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione or ethyl acetoacetate at room temperature or refluxing in ethanol. Alternatively, polysubstituted anilines were synthesized via a four component reaction of an aldehyde, a ketone, and two equivalents of malononitrile in ethanol.
Mass spec analysis was carried out using an Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Kyungpook National University, Dankook University, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, South Korea; Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, United States
Abstract
Sphingosine kinase1 (SphK1) is an acetyl-CoA dependent acetyltransferase which acts on cyclooxygenase2 (COX2) in neurons in a model of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, the mechanism underlying this activity was unexplored. Here we show that N-acetyl sphingosine (N-AS) is first generated by acetyl-CoA and sphingosine through SphK1. N-AS then acetylates serine 565 (S565) of COX2, and the N-AS-acetylated COX2 induces the production of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs). In a mouse model of AD, microglia show a reduction in N-AS generation, leading to decreased acetyl-S565 COX2 and SPM production. Treatment with N-AS increases acetylated COX2 and N-AS-triggered SPMs in microglia of AD mice, leading to resolution of neuroinflammation, an increase in microglial phagocytosis, and improved memory. Taken together, these results identify a role of N-AS in the dysfunction of microglia in AD.
Mass analysis was carried out using an Advion expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Authors: Japan Bioindustry Association, Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Japan
Highlights
- Deacetylation of glycopeptide with an esterase prevents base-induced side reactions, b-elimination, and epimerization
- An esterase from B. subtilis was utilized for Deacetylation of sugar hydroxyl groups on glycopeptide synthesis
- Deacetylation with an esterase and glycosylations with glycosyltransferases were accomplished in one-pot
Abstract
Glycopeptides are fragments of glycoproteins and are important in evaluating the biological roles of carbohydrates in glycoproteins. Fmoc solid-phase peptide synthesis using acetyl-protected glycosylated amino acids is a common strategy for the preparation of glycopeptides, but this approach normally requires chemical de-O-acetylation with a base that β-eliminates sugar residues and epimerizes the peptide backbone. Here we demonstrate a facile new chemoenzymatic synthetic strategy for glycopeptides, using an esterase for the de-O-acetylation of sugar residues and glycosyltransferases for successive sugar elongations at neutral pH.
ESI-MS spectra were collected using an Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) in negative ion mode.
The Advion Interchim Scientific suite of systems and consumables allows users to harness the power of mass spectrometry, flash chromatography, prep LC and more. Simple and robust, download our brochure to learn more about:
- The Advion Interchim Scientific expression® compact mass spectrometer (CMS): A fast and easy analytical tool for the organic chemist. Ideal for fast reaction monitoring, the expression® CMS features a single quadrupole that can adapt to multiple ionization sources in seconds, including both ESI and APCI. The expression® CMS offers a variety of novel sampling techniques, including fast assay methods for liquids, solids, gases, and even air-sensitive compounds.
- Direct mass analysis of TLC plates in 30 seconds at the push of a button with Plate Express™
- One-touch analysis of solids and liquid samples with the ASAP® probe
- LC/CMS
- puriFlash® ultra performance flash purification: Ideal for method development and purification of rare and high added value compounds, the Interchim family of puriFlash® systems offer users a wide range of throughput options and the highest recovery rates at >95%.
- Mass-Guided Purification: the Interchim puriFlash® + Advion CMS offers the ideal solution for Flash-MS, and can provide fraction identification in <30 seconds.
-
Fill out the form to download the full Advion Interchim Scientific brochure now.
Horbaczewskyj, Christopher Stefan (2019) Monitoring, Modelling and Optimisation of Continuous Flow Reactions Using On-line Mass Spectrometry. PhD thesis, University of Leeds.
Abstract
An on-line mass spectrometry method has been developed to monitor, model and optimise continuous flow reactions. This method makes use of dual-piston pumps, tubular reactor block, Vici sample actuator, an Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) and other analytical systems to investigate a variety of chemical systems based on their need for process improvement. Full reaction automation employed MATLAB, the Snobfit algorithm, along with Modde DoE software. On-line mass spectrometry has advantages over other analytical techniques as it has shorter acquisition times (2-60 s), low chemical sensitivity (~108 mol%) and chemical identity as well as the potential to provide quantitative information. In this work, reaction quantitation has been explored using four chemical systems, where each of them was monitored by a variety of analytical techniques, with the overall aim being to examine if on-line mass spectrometry can be used for quantitative analysis. For all cases investigated, process improvements were made whilst also determining optimal operating conditions to improve conversions, yields or selectivities as well as looking at reaction waste reduction. Flow chemistry and the work conducted has shown how waste can be reduced for certain reactions when compared to more traditional approaches. This method relies on machine learning, full process automation and quick process analytical technology to determine optimum conditions as well as build large reaction data sets. Large data sets were created using a hybrid DoE-kinetic composite circumscribed orthogonal design. Mass spectrometry provided valuable reaction information and has the potential for reaction quantitation depending on the required application, reaction system and ionisation settings. Compound thermal stability can be problematic in APCI+ mode whilst ion suppression is problematic in ESI+ mode. Still a versatile analytical tool, on-line mass spectrometry was found to be inherently quantitative. The continuous-flow-on-line-MS-self-optimisation platform was used to investigate a variety of different reactions to show versatility of the MS system. These reactions are summarized below. 1) An N-Boc deprotection of AZD5634 for optimisation and process scale-up, with achieved conversions >95% and scale-up to pilot and commercial scale using on-line mass spectrometry). 2) An N-Boc deprotection reaction using a hybrid DoE-kinetic model for optimisation and large data set generation, with achieved conversion >90%. 3) An SNAr reaction of AZD4547 for product selectivity and yield improvement, with achieved conversion of ~38% and DP yield of ~30%. 4) The synthesis and optimisation of Fe-N-heterocyclic carbene complexes using an electrochemical method for use in a C-H hydroxylation reaction. Optimum electrochemical conditions of either 7 V and 4 minutes residence time, or 2.5 V and 15 minutes residence were achieved.



