Institute of Food Research, Genome Analysis Center, Aix-Marseille University, University of East Anglia
Abstract
We previously identified and characterized an intramolecular trans-sialidase (IT-sialidase) in the gut symbiont Ruminococcus gnavus ATCC 29149, which is associated to the ability of the strain to grow on mucins. In this work we have obtained and analyzed the draft genome sequence of another R. gnavusmucin-degrader, ATCC 35913, isolated from a healthy individual. Transcriptomics analyses of both ATCC 29149 and ATCC 35913 strains confirmed that the strategy utilized by R. gnavus for mucin-degradation is focused on the utilization of terminal mucin glycans. R. gnavus ATCC 35913 also encodes a predicted IT-sialidase and harbors a Nan cluster dedicated to sialic acid utilization. We showed that the Nan cluster was upregulated when the strains were grown in presence of mucin. In addition we demonstrated that both R. gnavus strains were able to grow on 2,7-anyhydro-Neu5Ac, the IT-sialidase transglycosylation product, as a sole carbon source. Taken together these data further support the hypothesis that IT-sialidase expressing gut microbes, provide commensal bacteria such as R. gnavus with a nutritional competitive advantage, by accessing and transforming a source of nutrient to their own benefit.
Mass spectrometry analysis was performed on the Advion Interchim Scientific® expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) and the data was evaluated using Advion Interchim Scientific® Data Express software.
USDA, University of Connecticut
Abstract
Research methods that predict Fe bioavailability for humans can be extremely useful in evaluating food fortification strategies, developing Fe-biofortified enhanced staple food crops and assessing the Fe bioavailability of meal plans that include such crops. In this review, research from four recent poultry (Gallus gallus) feeding trials coupled with in vitro analyses of Fe-biofortified crops will be compared to the parallel human efficacy studies which used the same varieties and harvests of the Fe-biofortified crops. Similar to the human studies, these trials were aimed to assess the potential effects of regular consumption of these enhanced staple crops on maintenance or improvement of iron status. The results demonstrate a strong agreement between the in vitro/in vivo screening approach and the parallel human studies.
LC/MS analysis was complete using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS). Instrumentation and data acquisition were controlled by Advion Mass Express software
University of Florida, USDA, Kansas State University
Abstract
Currently, the global citrus production is declining due to the spread of Huanglongbing (HLB). HLB, otherwise known as citrus greening, is caused by Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus (CLas) and is transmitted by the Asian citrus psyllids (ACP), Diaphorina citri Kuwayama.
In this study, we investigated the micro- and macro-nutrients, nucleotides, and others secondary metabolites of phloem sap from pineapple sweet orange. The micro- and macro-nutrients were analyzed using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS) and inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES). Nucleotides and other secondary metabolites analysis was accomplished by reversed phase HPLC coupled with UV, fluorescence detection, or negative mode electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Gujarat University
Abstract
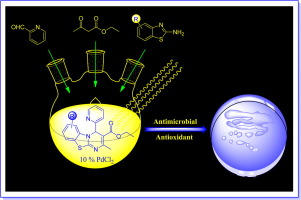
Synthesis of new and desired compounds has an everlasting demand. The present work emphasizes on the one pot, three component microwave assisted synthesis of novel ethyl 2-methyl-4-(pyridin-2-yl)-4H-benzo[4,5]thiazolo[3,2-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylate derivatives by the reaction of 2-aminobenzothiazole derivatives with Pyridine 2-aldehyde and Ethyl acetoacetate in the presence of PdCl2 as an expeditious catalyst under solvent-free condition.
The salient features of this approach are operational simplicity, convergence, short reaction time, high atom economy, easy workup, mild reaction conditions and environmentally benign conditions. All the newly synthesized diverse poly-functionalized tri-heterocyclic benzothiazole derivatives have been characterized by elemental analysis and various spectroscopic methods such as FT-IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, ESI-MS and Single crystal X-ray analysis (4a). All the final scaffolds have been screened for antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Also their antitubercular activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37RV was screened.
Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) analysis was performed using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Gujarat University
Abstract
A concise, facile and straightforward synthetic protocol has been described for the preparation of 6-amino-1,4-dihydropyrano[2,3-c]-pyrazole-5-carbonitrile derivatives by a one-pot, three-component reaction of ethyl acetoacetate, hydrazine hydrate, aryl aldehydes and malononitrile in glycerol as a green and reusable reaction media under catalyst free condition. The corresponding 6-amino-1,4-dihydropyrano[2,3-c]-pyrazole-5-carbonitriles have been obtained with good to excellent yields (86-92%). This protocol is highly efficient due to its mild reaction conditions, operational simplicity, use of inexpensive, eco-friendly and green reaction media, catalyst-free conditions and absence of toxic organic solvents.
Electrospray mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) was performed using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
University of Durham
Abstract
The synthesis of diazonium salts is historically an important transformation extensively utilized in dye manufacture. However the highly reactive nature of the diazonium functionality has additionally led to the development of many new reactions including several carbon-carbon bond forming processes. It is therefore highly desirable to determine optimum conditions for the formation of diazonium compounds utilizing the latest processing tools such as flow chemistry to take advantage of the increased safety and continuous manufacturing capabilities. Herein we report a series of flow-based procedures to prepare diazonium salts for subsequent in-situ consumption.
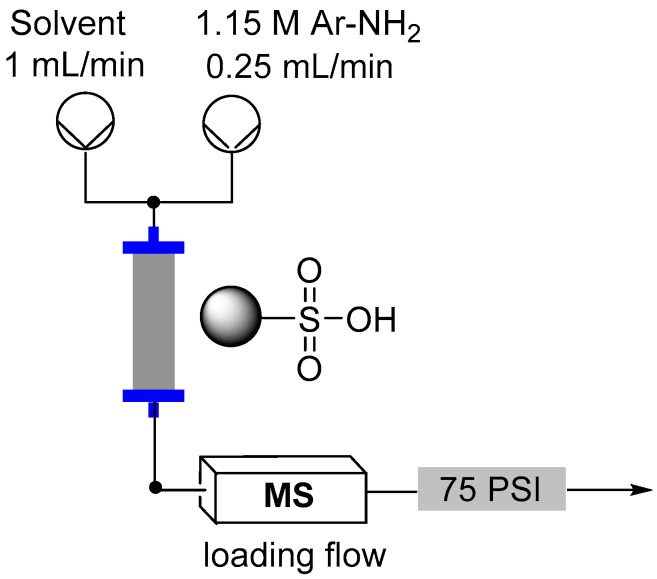
Flow reactor loading set-up.
Direct in-line mass spec analysis was performed using the Advion Interchim Scientific® expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) with electrospray ionization (ESI).
Western Washington University
Abstract
Sortase‐catalyzed transacylation reactions are widely used for the construction of non‐natural protein derivatives. However, the most commonly used enzyme for these strategies (sortase A from Staphylococcus aureus) is limited by its narrow substrate scope. To expand the range of substrates compatible with sortase‐mediated reactions, we characterized the in vitro substrate preferences of eight sortase A homologues.
From these studies, we identified sortase A enzymes that recognize multiple substrates that are unreactive toward sortase A from S. aureus.
We further exploited the ability of sortase A from Streptococcus pneumoniae to recognize an LPATS substrate to perform a site‐specific modification of the N‐terminal serine residue in the naturally occurring antimicrobial peptide DCD‐1L.
Finally, we unexpectedly observed that certain substrates (LPATXG, X=Nle, Leu, Phe, Tyr) were susceptible to transacylation at alternative sites within the substrate motif, and sortase A from S. pneumoniae was capable of forming oligomers. Overall, this work provides a foundation for the further development of sortase enzymes for use in protein modification.
Mass spectrometry analysis was performed using the Advion Interchim Scientific® expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Nirma University, India; Rega Institute for Medical Research
Abstract
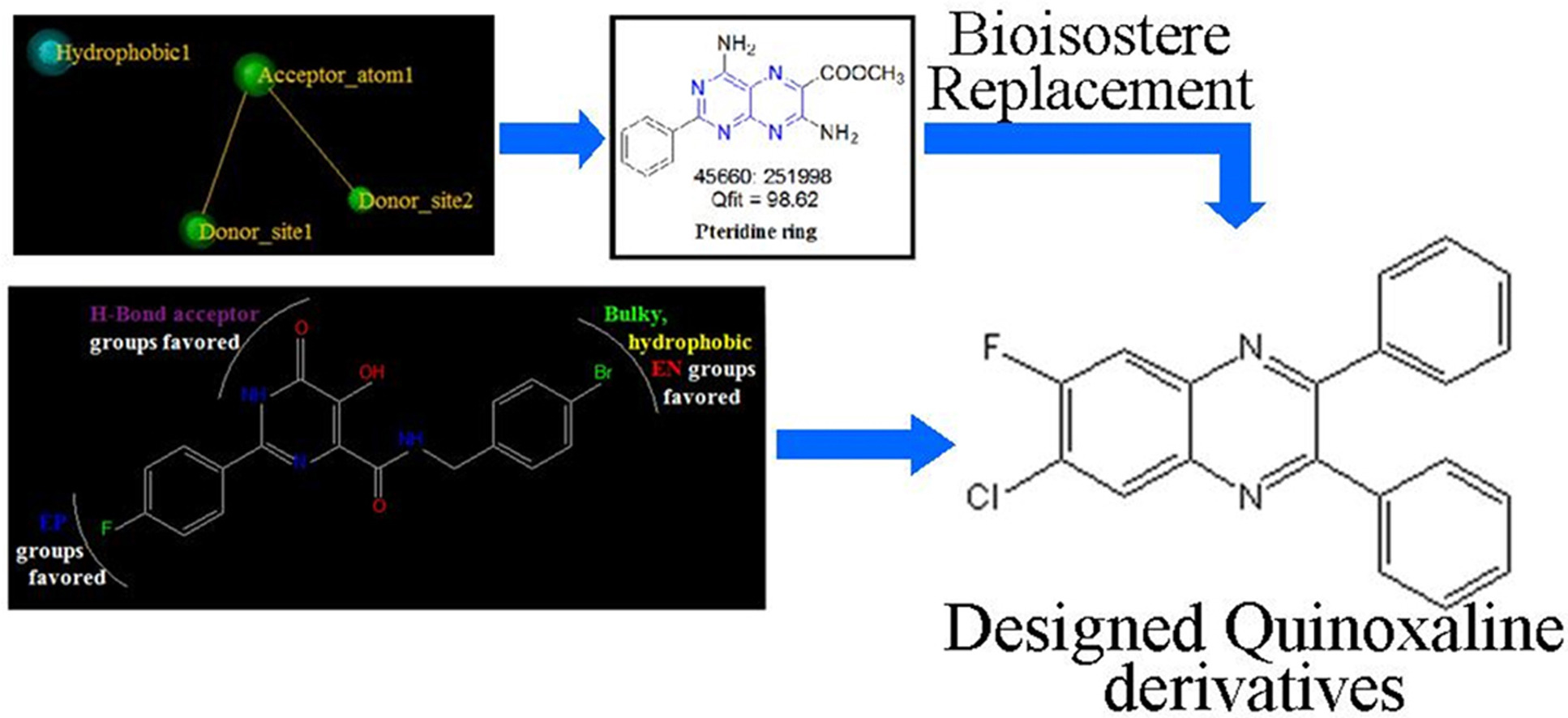
In order to design novel anti-HIV agents, pharmacophore modelling, virtual screening, 3D-QSAR and molecular docking studies were performed. 50 quinoxaline derivatives with different substitutions were designed on basis of both ligand based drug design approaches and were mapped on the best pharmacophore model. From this, best 32 quinoxaline derivatives were docked onto the active site of integrase enzyme and in-silico ADMET properties were also predicted. From this data, synthesis of top 7 quinoxaline derivatives was carried out and were characterized using Mass, 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectroscopy. Purity of compounds were checked using HPLC.
Two quinoxaline derivatives showed good results, which can be further explored to develop novel anti-HIV agents.
Lyon College, University of Rhode Island
Abstract
MOLSTR, Accepted manuscript. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2016.05.075
We have synthesized a trio of gallium complexes bearing 9-anthraldehyde thiosemicarbazones. The complexes were assessed for their anticancer activity and their biophysical reactivity was also investigated.
The results of docking studies with DNA, ribonucleotide reductase and human serum albumin, however showed that the complex with the best biological activity had the largest binding constant to DNA.
Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) was recorded using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Xention Limited, United Kingdom; University of Ljubljana, Slovenia
Abstract
The rodent neuroblastoma cell line, ND7-23, is used to express voltage-dependent sodium (Nav) and other neuronal ion channels resistant to heterologous expression in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) or human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells. Their advantage is that they provide endogenous factors and signaling pathways to promote ion channel peptide folding, expression, and function at the cell surface and are also amenable to automated patch clamping. However, ND7-23 cells exhibit endogenous tetrodotoxin (TTX)-sensitive Nav currents, and molecular profiling has revealed the presence of Nav1.2, Nav1.3, Nav1.6, and Nav1.7 transcripts, but no study has determined which subtypes contribute to functional channels at the cell surface. In this publication, we profiled the repertoire of functional Nav channels endogenously expressed in ND7-23 cells using the QPatch automated patch clamp platform and selective toxins and small molecules.
Mass spec analysis was performed using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).





