Authors: Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research, Germany; University of Twente, Netherlands
Abstract
We developed a simple way to create 2D conductive nanostructures with dielectric cores and conductive surfaces based on polyethylene with in-chain thiophene groups. Generally, thiophene-based polymers show great conductive properties, but exhibit a poor processability. Here, we use the crystallization of a polyethylene chain with precisely distributed thiophene groups as the platform for a self-organization of a lamellar structure. During crystallization, thiophene groups are expelled to the crystal surface. Subsequent copolymerization with 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene (EDOT) molecules finally yields 2D platelets with a conductive surface. The electric properties of the surface are demonstrated by conductivity measurements. Given the molecular structure of the polymer, it can be assumed that the conductive layer consists of only one monoatomic layer of polymerized thiophene. We thus show a new way to create an ultra-thin, conductive surface on a polymer surface in just a few steps. Hence, the method presented here opens up a wide range of possibilities to produce complex, nanoscale electronic structures for microelectronic applications.
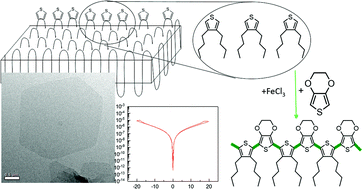
Mass spectrum analysis was obtained by ASAP/CMS using the Advion Interchim Scientific® ASAP® Atmospheric Solids Analysis Probe and expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS)
AstraZeneca, United Kingdom
Abstract
Deuterium exchange has been demonstrated to provide additional information to accurate mass measurement and collision‐induced dissociation on unknown chemical structures. An enhanced method for rapid deuterium exchange could make this technique more routine for structural elucidation. Open port sampling interface mass spectrometry (OPSI‐MS) with an aprotic solvent offers a rapid method for performing deuterium incorporation.
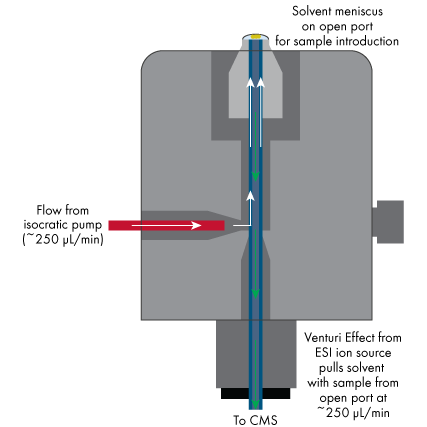
This publication features the Advion Interchim Scientific® Touch Express™ OPSI with the expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Institute of Food Research, Genome Analysis Center, Aix-Marseille University, University of East Anglia
Abstract
We previously identified and characterized an intramolecular trans-sialidase (IT-sialidase) in the gut symbiont Ruminococcus gnavus ATCC 29149, which is associated to the ability of the strain to grow on mucins. In this work we have obtained and analyzed the draft genome sequence of another R. gnavusmucin-degrader, ATCC 35913, isolated from a healthy individual. Transcriptomics analyses of both ATCC 29149 and ATCC 35913 strains confirmed that the strategy utilized by R. gnavus for mucin-degradation is focused on the utilization of terminal mucin glycans. R. gnavus ATCC 35913 also encodes a predicted IT-sialidase and harbors a Nan cluster dedicated to sialic acid utilization. We showed that the Nan cluster was upregulated when the strains were grown in presence of mucin. In addition we demonstrated that both R. gnavus strains were able to grow on 2,7-anyhydro-Neu5Ac, the IT-sialidase transglycosylation product, as a sole carbon source. Taken together these data further support the hypothesis that IT-sialidase expressing gut microbes, provide commensal bacteria such as R. gnavus with a nutritional competitive advantage, by accessing and transforming a source of nutrient to their own benefit.
Mass spectrometry analysis was performed on the Advion Interchim Scientific® expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) and the data was evaluated using Advion Interchim Scientific® Data Express software.
Gujarat University
Abstract
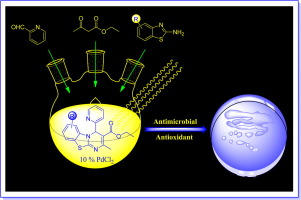
Synthesis of new and desired compounds has an everlasting demand. The present work emphasizes on the one pot, three component microwave assisted synthesis of novel ethyl 2-methyl-4-(pyridin-2-yl)-4H-benzo[4,5]thiazolo[3,2-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxylate derivatives by the reaction of 2-aminobenzothiazole derivatives with Pyridine 2-aldehyde and Ethyl acetoacetate in the presence of PdCl2 as an expeditious catalyst under solvent-free condition.
The salient features of this approach are operational simplicity, convergence, short reaction time, high atom economy, easy workup, mild reaction conditions and environmentally benign conditions. All the newly synthesized diverse poly-functionalized tri-heterocyclic benzothiazole derivatives have been characterized by elemental analysis and various spectroscopic methods such as FT-IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, ESI-MS and Single crystal X-ray analysis (4a). All the final scaffolds have been screened for antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Also their antitubercular activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37RV was screened.
Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) analysis was performed using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Gujarat University
Abstract
A concise, facile and straightforward synthetic protocol has been described for the preparation of 6-amino-1,4-dihydropyrano[2,3-c]-pyrazole-5-carbonitrile derivatives by a one-pot, three-component reaction of ethyl acetoacetate, hydrazine hydrate, aryl aldehydes and malononitrile in glycerol as a green and reusable reaction media under catalyst free condition. The corresponding 6-amino-1,4-dihydropyrano[2,3-c]-pyrazole-5-carbonitriles have been obtained with good to excellent yields (86-92%). This protocol is highly efficient due to its mild reaction conditions, operational simplicity, use of inexpensive, eco-friendly and green reaction media, catalyst-free conditions and absence of toxic organic solvents.
Electrospray mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) was performed using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
University of Durham
Abstract
The synthesis of diazonium salts is historically an important transformation extensively utilized in dye manufacture. However the highly reactive nature of the diazonium functionality has additionally led to the development of many new reactions including several carbon-carbon bond forming processes. It is therefore highly desirable to determine optimum conditions for the formation of diazonium compounds utilizing the latest processing tools such as flow chemistry to take advantage of the increased safety and continuous manufacturing capabilities. Herein we report a series of flow-based procedures to prepare diazonium salts for subsequent in-situ consumption.
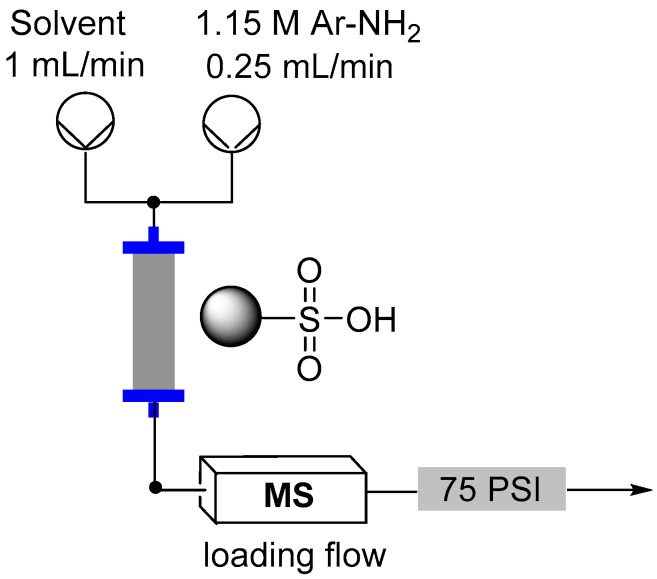
Flow reactor loading set-up.
Direct in-line mass spec analysis was performed using the Advion Interchim Scientific® expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) with electrospray ionization (ESI).
Xention Limited, United Kingdom; University of Ljubljana, Slovenia
Abstract
The rodent neuroblastoma cell line, ND7-23, is used to express voltage-dependent sodium (Nav) and other neuronal ion channels resistant to heterologous expression in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) or human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells. Their advantage is that they provide endogenous factors and signaling pathways to promote ion channel peptide folding, expression, and function at the cell surface and are also amenable to automated patch clamping. However, ND7-23 cells exhibit endogenous tetrodotoxin (TTX)-sensitive Nav currents, and molecular profiling has revealed the presence of Nav1.2, Nav1.3, Nav1.6, and Nav1.7 transcripts, but no study has determined which subtypes contribute to functional channels at the cell surface. In this publication, we profiled the repertoire of functional Nav channels endogenously expressed in ND7-23 cells using the QPatch automated patch clamp platform and selective toxins and small molecules.
Mass spec analysis was performed using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Gujarat University
Abstract
A library of thiosemicarbazide hybrid 2-(aldo-polyhydroxyalkyl)benzimidazole derivatives have been designed and synthesized with simple and eco-friendly methodologies. The structures of the compounds have been elucidated with the aid of elemental analysis, IR, mass and 1H NMR spectral data. These novel synthesized compounds have been evaluated for their antibacterial activity against two gram-positive bacteria (S. aureus and S. pyogenus) and two gram-negative bacteria (P. aeruginosa and E. coli). The title compounds have also been studied for their antifungal activity against C. albicans, A. niger and A. clavatus using the broth dilution technique.
Mass spec analysis was performed using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) with electrospray ionization (ESI).
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
Abstract
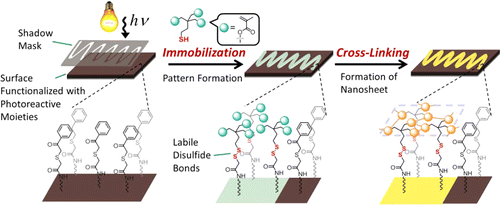
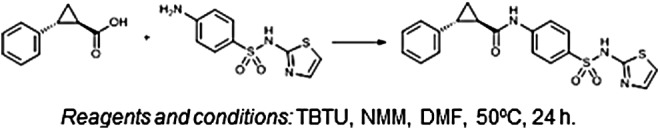
The preparation of cross-linked nanosheets with 1–2 nm thickness and predefined shape was achieved by lithographic immobilization of trimethacryloyl thioalkanoates onto the surface of Si wafers, which were functionalized with 2-(phenacylthio)acetamido groups via a photoinduced reaction. Subsequent cross-linking via free radical polymerization as well as a phototriggered Diels–Alder reaction under mild conditions on the surface led to the desired nanosheets. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS), as well as infrared reflection-absorption spectroscopy (IRRAS) confirmed the success of individual surface-modification and cross-linking reactions.
ESI-MS analysis was performed using the Advion Interchim Scientific® expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
Gujarat University
Abstract
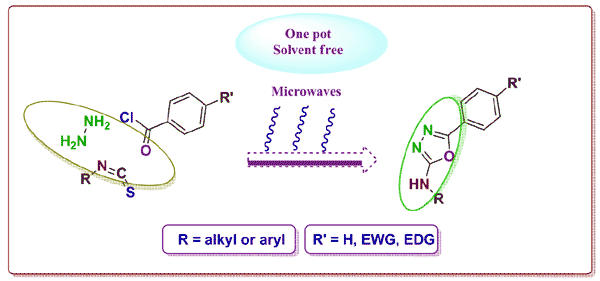
A convenient one-pot, multi-component and solvent free procedure for the preparation of substituted 2-amino-5-aryl-1,3,4-oxadiazoles has been achieved. The method is a significant improvement over previously reported synthesis. Reaction of acid chlorides with hydrazine hydrate and isothiocynates under microwave-irradiation (MWI) afforded the corresponding 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives in high yields with high purity. All synthesized compounds were characterized by FT-IR, proton and carbon NMR, mass spectroscopy and elemental analysis. A possible mechanism is proposed for the cyclodesulfurization based on the results of this study.
Mass spec analysis was performed on the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) using electrospray ionization (ESI).







