Mokpo National University, Gachon University, Hanyang University, Gachon Medical Research Institute, South Korea; University of Bremen, Germany
Abstract
G protein-coupled receptor (GPR) 119 is expressed in pancreatic β-cells and intestinal L cells, and is involved in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) release, respectively. Therefore, the development of GPR119 agonists is a potential treatment for type 2 diabetes. In this publication, screened 1500 natural plant extracts for GPR119 agonistic actions and investigated the most promising extract, that from Angelica dahurica (AD), for hypoglycemic actions in vitro and in vivo.
Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) data was measured using the Advion expression CMS
Justus Liebig University Giessen, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia
Abstract
Effect-directed analysis (EDA) by the combination of high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) with biologi- cal and enzymatic assays represents one of the latest tools available for the rapid bioprofiling of complex matrices, such as plant extracts. In this ambit, the aim of this project was the non-targeted screening of inflorescence extracts from ten different hemp varieties for components exhibiting radical scavenging, antibacterial, enzyme inhibiting and estrogen-like effects.
The characterization of two prominently multipotent bioactive com- pound zones was finally achieved by HPTLC-HRMS and preliminary assigned as cannabidiolic acid and cannabidivarinic acid.
HTPLC analysis was coupled via the Advion Plate Express® TLC Plate Reader.
Cornell University, Kaiser Permanente Fontana, Bar-Ilan University
Abstract
The consumption of teff (Eragrostis tef), a gluten-free cereal grain, has increased due to its dense nutrient composition including complex carbohydrates, unsaturated fatty acids, trace minerals (especially Fe), and phytochemicals. This study utilized the clinically-validated Gallus gallus intra amniotic feeding model to assess the effects of intra-amniotic administration of teff extracts versus controls using seven groups: (1) non-injected; (2) 18Ω H2O injected; (3) 5% inulin; (4) teff extract 1%; (5) teff extract 2.5%; (6) teff extract 5%; and (7) teff extract 7.5%. The treatment groups were compared to each other and to controls. Our data demonstrated a significant improvement in hepatic iron (Fe) and zinc (Zn) concentration and LA:DGLA ratio without concomitant serum concentration changes, up-regulation of various Fe and Zn brush border membrane proteins, and beneficial morphological changes to duodenal villi and goblet cells. No significant taxonomic alterations were observed using 16S rRNA sequencing of the cecal microbiota. Several important bacterial metabolic pathways were differentially enriched in the teff group, likely due to teff’s high relative fiber concentration, demonstrating an important bacterial-host interaction that contributed to improvements in the physiological status of Fe and Zn. Therefore, teff appeared to represent a promising staple food crop and should be further evaluated.
Analysis was performed by LC/MS using the Advion Interchim Scientific expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
University of North Texas, Huazhong Agricultural University, Heinrich Heine University, University of Goettingen, Leibniz Institute of Plant Genetics & Crop Plant Research, USDA-ARS
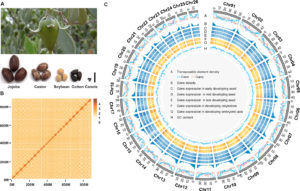
Abstract
Seeds of the desert shrub, jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis), are an abundant, renewable source of liquid wax esters, which are valued additives in cosmetic products and industrial lubricants. Jojoba is relegated to its own taxonomic family, and there is little genetic information available to elucidate its phylogeny. Here, we report the high-quality, 887-Mb genome of jojoba assembled into 26 chromosomes with 23,490 protein-coding genes. The jojoba genome has only the whole-genome triplication (γ) shared among eudicots and no recent duplications. These genomic resources coupled with extensive transcriptome, proteome, and lipidome data helped to define heterogeneous pathways and machinery for lipid synthesis and storage, provided missing evolutionary history information for this taxonomically segregated dioecious plant species, and will support efforts to improve the agronomic properties of jojoba.
NanoESI-MS/MS and UPLC-nanoESI-MS/MS methods using the Advion TriVersa NanoMate were used to analyze triacylglycerols from jojoba.
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique used to determine the mass-to-charge ratio of ions in a sample and therefore the sample composition. This method is used across many industries including food and beverage, environmental monitoring, and clinical. There are many features of mass spectrometers that must be considered before purchasing such as the required mass analyzer technology, ionization source, and dissociation technique. Join Lab Manager and our panel of experts as we discuss how to decipher mass spectrometry technology offerings and find the right solution for your lab.
As an attendee, you will learn more about:
- Available technology for performing mass spectrometry
- Features to consider when purchasing mass spectrometry instruments
- How to find the right mass spectrometer for your application
Environmental monitoring is vital to understanding the world around us. Air quality, water, and soil testing all provide valuable information about an environment’s status. Tools and technologies for environmental monitoring can be used to evaluate the sanitation of a food and beverage lab or to monitor an ecosystem’s recovery after an oil spill. Join Lab Manager and our panel of experts as we review the tools available for environmental testing and monitoring.
As an attendee, you will learn more about:
- Developments in technology for environmental testing and monitoring
- Considerations when purchasing technology for environmental testing and monitoring
- Applications for environmental testing and monitoring across industries
This webinar was hosted by Lab Manager Tech Trends and recorded July 9, 2020.
A simple, sensitive and selective ASAP® sample introduction approach to measuring the presence of two isobaric compounds, CBDA and THCA, contained in a complex sample such as hemp or cannabis plants or their corresponding extraction products. Measurements are made of differences in the relative composition of CBDA and THCA fragment ions originating from the same precursor ion. Applicability to screening plants and plant product materials such as hemp or marijuana to monitor out-of-specification composition is demonstrated.
This application was developed from the poster presented at the 2018 Cannabis Science Conference in Portland, OR.
Review new data and tips for using the Advion Interchim Scientific SOLATION® inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS) in the cannabis and hemp testing lab, and factors that affect heavy metals in cannabis and hemp.
This ebook was created with Spectroscopy and released June 2020.
Dr. Jack Henion presents the possibility of using the Advion Interchim Scientific expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) for ‘roadside breath testing’ of THC DRUID (driving under the influence of drugs) with the use of a small plastic breath collection device from Breath Explor of Uppsala, Sweden. This device serves as a simple, acceptable collection device for individuals in contrast to venous puncture with a needle or other means of collecting a biological sample.
In this ASMS 2020 Reboot presentation, you will learn:
- Breath sample collection with the Breath Explor device
- The potential benefits and challenges of a roadside LC/CMS testing system including an automated robot for sample preparation with the Advion Interchim Scientific expression® CMS and Advion Interchim Scientific AVANT UHPLC
- The Advion LC/CMS system provides accurate and sensitive results when used to analyze breath samples for THC
Authors: Olof Beck2, Jack Henion1, Sabina Seferaj2, Peter Stamback3
1Advion, Inc., Ithaca, NY
2Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden
3Breath Explore, Munkplast AB, Uppsala, Sweden
Patulin is a mycotoxin that is a common contaminant in food and animal feed, especially in apple products. The potential health risk of patulin to humans led to the establishment of action levels in foodstuffs.
The EU, WHO and US FDA defined maximum levels of patulin in fruit juices. The EU also has specific regulations for solid apple products and foods intended for infants and young children such as apple compote.
In this application note, a simple UHPLC/CMS method using the Advion Interchim Scientific AVANT® UHPLC and expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) system is introduced for the analysis of patulin in apple juice and apple compotes.
The research presented in this application note was a poster presentation for ASMS 2020 Reboot.

