North University of China, Lvliang College
Abstract
In this study, total saponins were extracted from Pleurotus ostreatus cultivated with Astragalus as one of organic culture substrates. High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography (HPTLC) assay showed total saponins could be separated effectively, and four kinds of spots were identified as AG I, AG II, AG III, and AG IV, respectively. FTIR spectra based on HPTLC separation assay showed the saponin characteristic groups including ‐OH, C‐H, C=O, and the glycoside linkaged to sapogenin group C‐O‐C, suggesting the four kinds of spots belonged to cycloartane‐type triterpene saponins. The primary mass spectra of precursor ion (HPTLC‐ESI‐MS) assay further proved the main composition of four kinds of spots was AG I‐IV, respectively. Physical properties, including the detection of specific rotation and melting point, revealed the separation of high‐purity saponin monomer by HPTLC. HPTLC‐dual wavelength spectrodensitometric method detection showed that content of astragaloside I‐IV was ranged from 0.2 to 0.5 mg/g, and the total astragalosides contents attained to 1.397 mg/g, indicating P. ostreatus could bioaccumulate astragalosides from Astragalus. These results demonstrated the characterization of astragalosides based on the separation of HPTLC was effective, and supported to consider astragalosides‐enriched P. ostreatus as functional edible fungus for food and medical applications.
Practical Application
Currently, the consumption of enriched foods has become common and continues to increase due to urgent demanding for foods with high nutritional value. Pleurotus ostreatus is a functional edible fungus, which not only can produce secondary metabolites, but can enrich bioactive ingredients. Astragalosides have a wide range of biological activities, especially currently being tested as cardioprotective agent. In this study, P. ostreatus was cultivated through adding Astragalus into culture substrates, which realized massive enrichment of astragalosides. Astragalosides‐enriched P. ostreatus as functional edible fungus could be extensively used in food and medical areas, especially for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
Analysis was performed by LC/MS using the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
University of North Texas, Huazhong Agricultural University, Heinrich Heine University, University of Goettingen, Leibniz Institute of Plant Genetics & Crop Plant Research, USDA-ARS
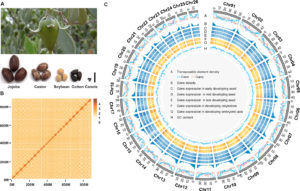
Abstract
Seeds of the desert shrub, jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis), are an abundant, renewable source of liquid wax esters, which are valued additives in cosmetic products and industrial lubricants. Jojoba is relegated to its own taxonomic family, and there is little genetic information available to elucidate its phylogeny. Here, we report the high-quality, 887-Mb genome of jojoba assembled into 26 chromosomes with 23,490 protein-coding genes. The jojoba genome has only the whole-genome triplication (γ) shared among eudicots and no recent duplications. These genomic resources coupled with extensive transcriptome, proteome, and lipidome data helped to define heterogeneous pathways and machinery for lipid synthesis and storage, provided missing evolutionary history information for this taxonomically segregated dioecious plant species, and will support efforts to improve the agronomic properties of jojoba.
NanoESI-MS/MS and UPLC-nanoESI-MS/MS methods using the Advion TriVersa NanoMate were used to analyze triacylglycerols from jojoba.
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique used to determine the mass-to-charge ratio of ions in a sample and therefore the sample composition. This method is used across many industries including food and beverage, environmental monitoring, and clinical. There are many features of mass spectrometers that must be considered before purchasing such as the required mass analyzer technology, ionization source, and dissociation technique. Join Lab Manager and our panel of experts as we discuss how to decipher mass spectrometry technology offerings and find the right solution for your lab.
As an attendee, you will learn more about:
- Available technology for performing mass spectrometry
- Features to consider when purchasing mass spectrometry instruments
- How to find the right mass spectrometer for your application
Lab Manager Tech Trends Webinar. Recorded June 25, 2020.
Food and beverage labs use techniques from other disciplines such as microbiology, environmental monitoring, and analytical chemistry to test for food and beverage contaminants. Unlike these disciplines, the food and beverage industry is highly regulated and therefore food and beverage labs have very specific needs. Join Lab Manager and our panel of experts as we discuss tools for food and beverage testing.
In this webinar, you will learn more about:
- The latest technology for testing in the food and beverage lab
- Applications for tools and technologies in the food and beverage lab
- Considerations when purchasing instruments for food and beverage testing
Patulin is a mycotoxin that is a common contaminant in food and animal feed, especially in apple products. The potential health risk of patulin to humans led to the establishment of action levels in foodstuffs.
The EU, WHO and US FDA defined maximum levels of patulin in fruit juices. The EU also has specific regulations for solid apple products and foods intended for infants and young children such as apple compote.
In this application note, a simple UHPLC/CMS method using the Advion Interchim Scientific AVANT® UHPLC and expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) system is introduced for the analysis of patulin in apple juice and apple compotes.
The research presented in this application note was a poster presentation for ASMS 2020 Reboot.
Patulin is a mycotoxin that is a common contaminant in food and animal feed, especially in apple products. The potential health risk of patulin to humans led to the establishment of action levels in foodstuffs.
The EU, WHO and US FDA defined maximum levels of patulin in fruit juices. The EU also has specific regulations for solid apple products and foods intended for infants and young children such as apple compote.
In this poster, a simple UHPLC/CMS method using the Advion AVANT UHPLC and expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) system is introduced for the analysis of patulin in apple juice and apple compotes.
This poster was presented at the ASMS 2020 Reboot.
USDA-ARS, Cornell University, Michigan State University
Abstract
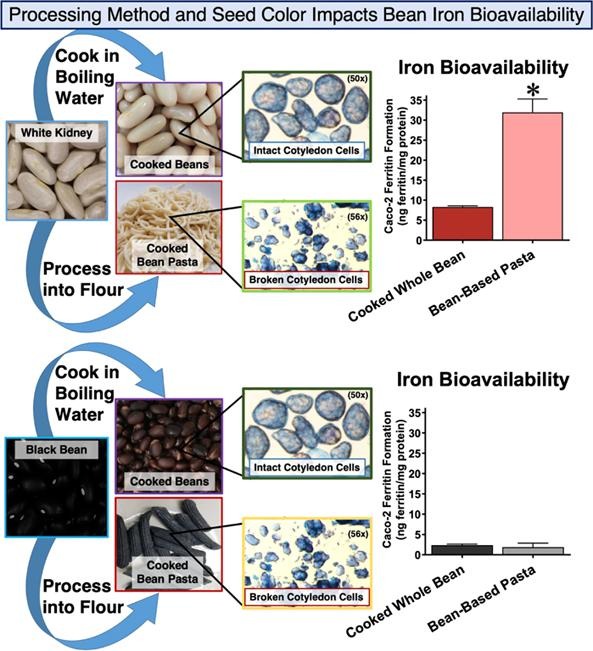
Processing techniques can disrupt the cotyledon cell walls of raw beans, allowing digestive enzymes greater access to intercellular stores of micronutrients such as iron during digestion. This study evaluated the iron bioavailability of seven bean varieties with different seed coat colors (white, yellow, cranberry, red, black) either boiled or processed into spaghetti pastas formulated from heat treated bean flour as the major ingredient (90% bean flour). Iron bioavailability was significantly (p ≤ 0.05) higher in spaghetti made from white or yellow bean varieties Snowdon, Alpena, Samurai and Canario when compared to boiled beans. Although cotyledon cells were broken and the phytate to iron molar ratios were significantly lower, the iron bioavailability of the cranberry (Etna), red kidney (Red Hawk) and black (Zenith) bean varieties did not improve after processing into spaghetti. Iron bioavailability of bean-based pastas was associated with procyanidin and cinnamtannin compounds that have a negative impact on the absorption of iron.
Analysis was performed by LC/MS using the Advion Interchim Scientific expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS).
In this application note, the Advion Interchim Scientific expression® Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) with volatile APCI (vAPCI) is used to analyze volatile compounds present during the fermentation of homebrewed beer by Stephanie Rankin Turner of Loughborough University.
The complex flavor of beer is primarily a result of the ingredients used, the brewing method, and conditions during fermentation. The analysis of beer throughout this process can be invaluable. Being one of the most widely consumed beverages worldwide, rapid and reliable analytical techniques are essential to keep up with demand and production.
This note demonstrates the use of the Advion Interchim Scientific expression® CMS with vAPCI for the analysis of volatile compounds from the headspace of homebrew beer and hops. The Venturi-assisted interface of the instrument enabled rapid sampling of volatiles, allowing the changing volatile profile of the homebrew to be observed throughout the fermentation process. This simple method would be suitable for fast quality control during alcoholic beverage production.
The Advion Interchim Scientific suite of systems and consumables allows users to harness the power of mass spectrometry, flash chromatography, prep LC and more. Simple and robust, download our brochure to learn more about:
- The Advion Interchim Scientific expression® compact mass spectrometer (CMS): A fast and easy analytical tool for the organic chemist. Ideal for fast reaction monitoring, the expression® CMS features a single quadrupole that can adapt to multiple ionization sources in seconds, including both ESI and APCI. The expression® CMS offers a variety of novel sampling techniques, including fast assay methods for liquids, solids, gases, and even air-sensitive compounds.
- Direct mass analysis of TLC plates in 30 seconds at the push of a button with Plate Express™
- One-touch analysis of solids and liquid samples with the ASAP® probe
- LC/CMS
- puriFlash® ultra performance flash purification: Ideal for method development and purification of rare and high added value compounds, the Interchim family of puriFlash® systems offer users a wide range of throughput options and the highest recovery rates at >95%.
- Mass-Guided Purification: the Interchim puriFlash® + Advion CMS offers the ideal solution for Flash-MS, and can provide fraction identification in <30 seconds.
-
Fill out the form to download the full Advion Interchim Scientific brochure now.
In this Lab Manager webinar, Dr. Daniel Eikel, Advion Director of Product Applications and Customer Service reviews the use of the Advion expression Compact Mass Spectrometer (CMS) for food and beverage analysis.
As an attendee, you will learn more about:
- How leading technologies and techniques affect food science researchers
- How to establish workflows that optimize the efficiency of your food science lab
- New and novel applications in the field of food and beverage science


